Introduction and background Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratiosClosure of mesenteric defects increased the risk for severe postoperative complications (54 4·3% for closure vs 35 2·8% for nonclosure, odds ratio 1·55, 95% CI 1·01–2·39, p=0·044), mainly because of kinking of the jejunojejunostomy Why does the analysis of reoperation due to small bowel obstruction use hazard ratio, and theUseful when the risk is not constant with respect to time It uses information collected at different times The
Odds Ratio Vs
Odds ratio vs hazard ratio interpretation
Odds ratio vs hazard ratio interpretation- In the RCT example, the hazard ratio was 080 (table 2a), virtually the same as the rate ratio The interpretation of the hazard ratio is also similar to the rate ratio the hazard of a poor outcome in the group treated with aspirin and dipyramidole is 080 times the hazard in the group treated with aspirin alone, a relative reduction of %Entities based on odds and hazard ratios When events in the intervention group are significantly less frequent than in the control group, then relative risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio (and their confidence intervals) will be less than 10 If the converse holds true, these values will




Odds Ratios Ors From The Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis Download Scientific Diagram
95% confidence interval, 025 to 047;However, you can calculate an odds ratio and interpret it as an approximation of the risk ratio, particularly when the disease is uncommon in the population Exercise 38 Calculate the odds ratio for the tuberculosis data in Table 312 Would you say that your odds ratio is an accurate approximation of the risk ratio?A significant benefit was also observed with respect to the confirmed objective response rate and the time to
The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programRelative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the help of examples The interpretation of each is presented in plain English rather than in technical language Clinically useful notes are provided, wherever necessary J Clin Psychiatry 15;76(7)e8571 Log hazard ratio of dropout from the maintenance treatment program between patients in clinics B and A who take 50mg dose of methadone 2 Log hazard ratio of dropout from the maintenance treatment program between two individuals who are at clinic A and whose dosage differs by 1 mg 3 Difference in log hazard ratio of dropout from the
You interpret an odds ratio the same way you interpret a risk ratio An odds ratio of 15 means the odds of the outcome in group A happening are one and a half times the odds of the outcome happening in group B Hazard ratio A hazard ratio (HR) is an annual risk of death (or some other outcome, eg, cancer recurrence, heart attack) over aThe second odds ratio is a summary across whatever stratumspecific odds ratios are available; Interpretation of Hazard Ratio Because Hazard Ratio is a ratio, then when HR = 05 at any particular time, half as many patients in the treatment group are experiencing an event compared to the control group HR = 1 at any particular




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference The Journal Of Family Practice Data Science Study Plan Clinical Trials




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
Hazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period Please note that results shown are rounded to 2 decimal places, but the calculations used the raw numbers from the previous column ( c ) and therefore give different results than if the rounded numbers were used (eg, 006/008 = 075)To understand what an odds ratio means in terms of changes in numbers of events it is simplest to first convert it into a risk ratio, and then interpret the risk ratio in the context of a typical control group risk, as outlined above The formula for converting an odds ratio to a risk ratio is provided in Chapter 12 (Section Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




In A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Estimates From Observational Studies Can I Pool Or With Hr And Rr Probably Not How Can I Transform Hr To Or
Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposure Relative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) group Is hazard ratio and odds ratio?Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) In casecontrol studies, and So, the rate ratio was 047 Interpretation Women who used postmenopausal hormones had 047 times the rate of coronary artery disease compared to women who did not use postmenopausal hormones (Rate ratios are often interpreted as if they were risk ratios, eg, postmenopausal women using HRT had 047 times the risk of CAD compared to women




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download
RR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to pat Odds = P (positive) / 1 – P (positive) = (42/90) / 1 (42/90) = (42/90) / (48/90) = 0875 Thus, the odds ratio for experiencing a positive outcome under the new treatment compared to the existing treatment can be calculated as Odds Ratio = 125 / 0875 = 1428 We would interpret this to mean that the odds that a patient experiences aThe odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group An RR (or OR) of 10 indicates that there is no difference in risk (or odds) between the groups being compared




Statistics 103 Monday July 10 17 Survival Analysis



2
The odds ratio is simply the ratio between the following two ratios The ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who died, and the ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who survived From the data in the table 1, it is calculated as follows OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (152/17)/We would interpret this to mean that the odds that a player passes the test by using the new program are 144 times the odds that a player passes the test by using the old program In other words, the odds that a player passes the testLogistic regression log (odds) = The way to interpret the exposure coefficient, exposure is some surgery (vs no surgery), the hazard ratio of death may take values as follows Time since baseline Hazard ratio 1 day 9 2 days 35




Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
Cox regression vs logistic regression Distinction between hazard/rate ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precisionOdds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples of RR and OR for different probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 RR OR4 1 4 62 3 67 5804 01 4 03 67 66 Hazard ratio (HR) Broadly equivalent to relative risk (RR);The method of presenting the results of clinical studies can affect their interpretation by clinicians2 and nonclinicians alike3,4 Therefore, it is important to understand the different ways in which results can be presented Absolute risk refers to the simple event rate in a group of people who




Main Results Of The Comparison Between The Hazard Ratio Hr Odds Download Table




Meta Analysis Odds Ratio
Risk (hazard) ratios and odds ratios cannot be used interchangeably in metaanalysis Like euro and pound they have to be converted into the same value eg Swedish crowns You find theStart studying Risk Ratio, Odds Ratio, KaplanMeier, Survival Analysis, Hazard Analysis Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像
This corresponds to a MantelHaenszel–adjusted odds ratio of 50 for Table 4 and 279 for Table 5 However, all of these odds ratios lack any interpretation as an average In cohort A, imagingbased progressionfree survival was significantly longer in the olaparib group than in the control group (median, 74 months vs 36 months;Odds Ratio (OR) vs A hazard ratio is
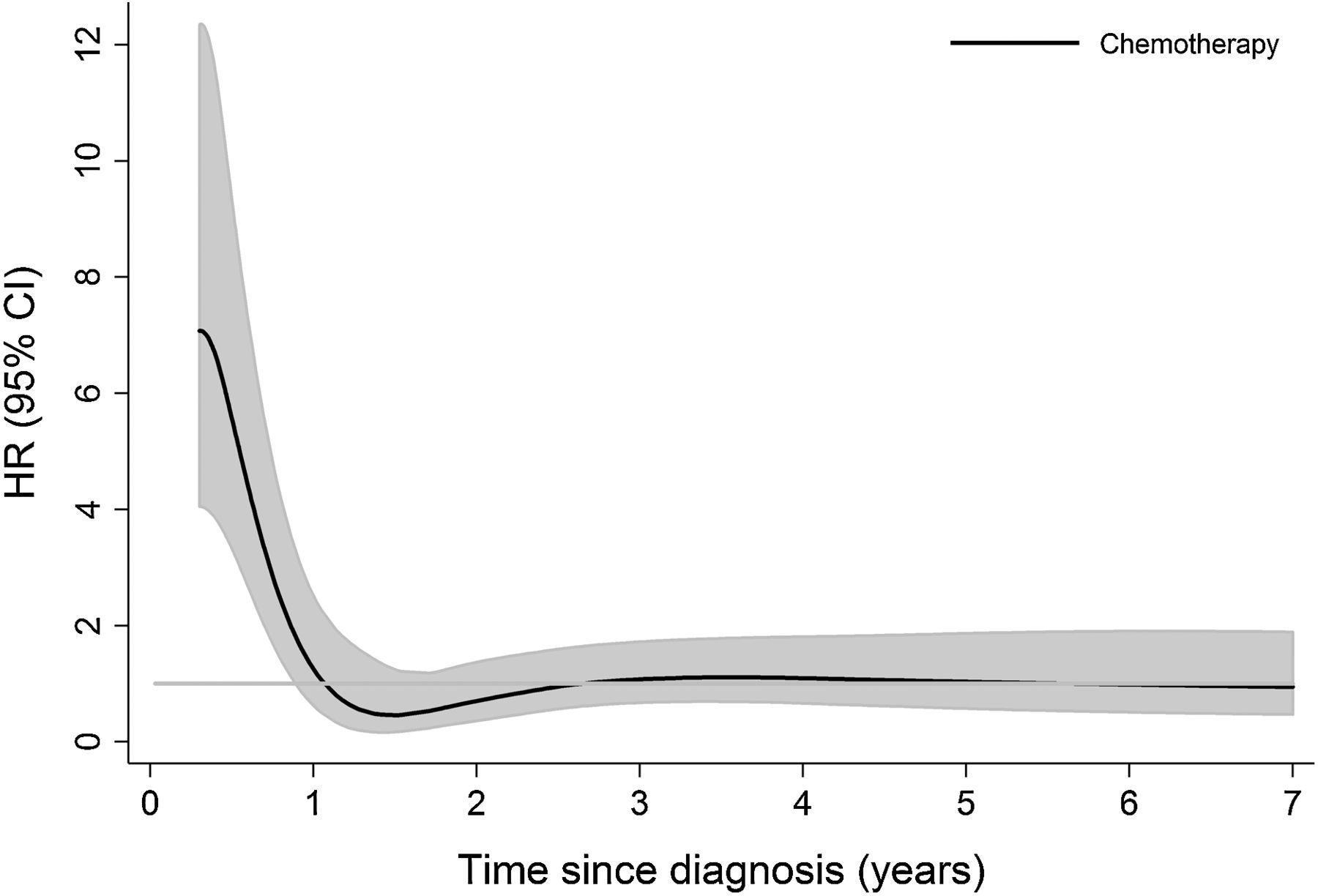



Hazard Ratio Plots With Non Linear Time Varying Effects In R Survival Analysis Datamethods Discussion Forum



2
Nelsonlen cumulative hazard estimates, by group analysis time 0 10 30 40 000 100 0 300 400 group 0 group 1 Hazard Ratio = 71 KaplanMeier survival estimates, by group analysis time 0 10 30 40 000 025 050 075 100 group 0 group 1 Title Point Estimation Odds Ratios, Hazard Ratios/Rates, Risk Differences,Precision Author The interpretation of a hazard ratio is essentially the same as an odds ratio However it's probably worth noting that whilst an odds ratio is derived from calculating the odds of an event in the intervention and the control arms expressed as a ratioLead authors of studies reporting hazard ratio results were contacted to obtain raw data or alternative analysis results (eg, odds ratios) to allow all 11 studies to be analyzed together




Logistic Regression And Survival Analysis




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
Variable on the hazard or risk of an event Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposureRelative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) group Let's say that in your experiment the calculated Hazard Ratio is equal to 065 This is how you can interpret and report it The mortality rate in a group of smokers drops by 35% compared to the group of highcalorie diet The mortality rate among smokers is 065 times of that among patients with a highcalorie dietP less than 0001);
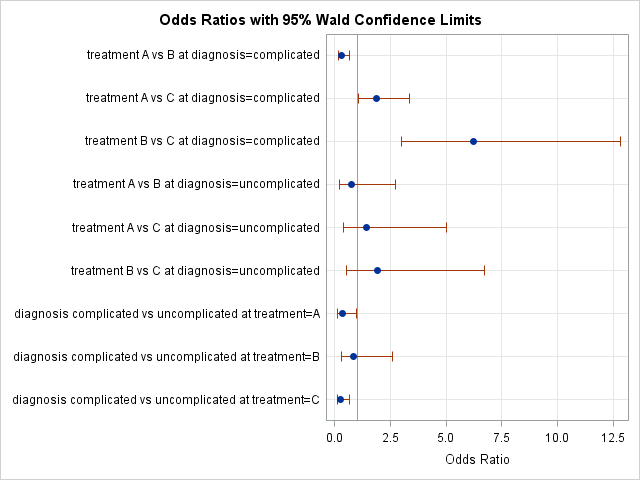



Odds Ratio Plots With A Logarithmic Scale In Sas The Do Loop




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp
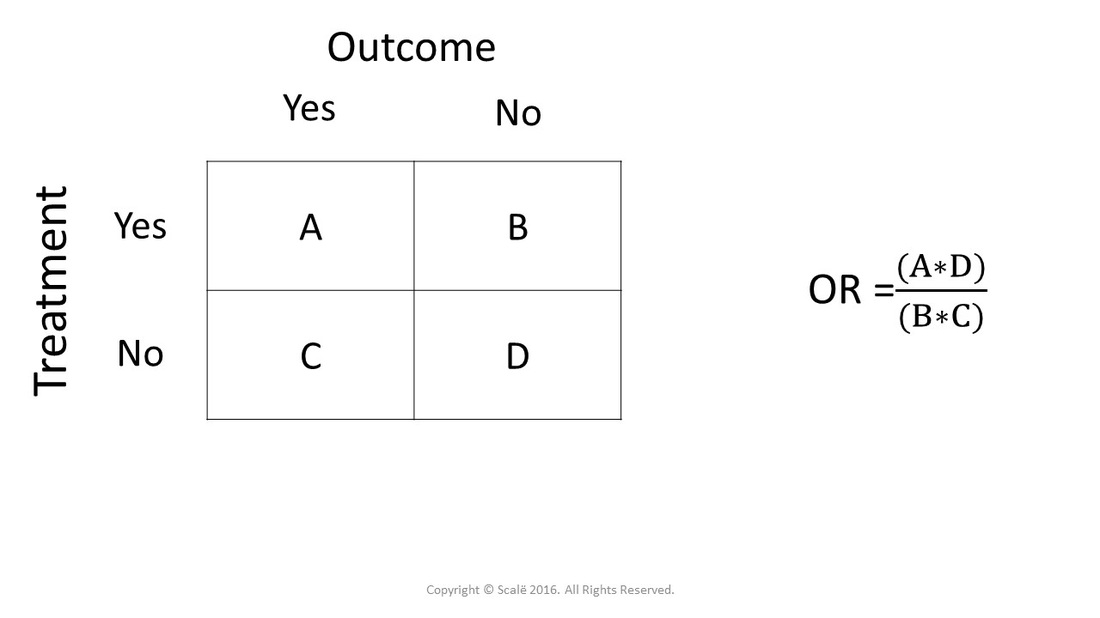
The odds ratio is calculated as Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C) Odds ratio = (61*48) / (39*52) Odds ratio = 144;Peto's method applied to dichotomous data (Section 9442) gives rise to an odds ratio;Hazard ratio vs relative risk How to explain the difference between hazard ratio and In survival analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) is the ratio of the hazard rates corresponding to the conditions described by two levels of an explanatory variable For example, in a drug study, the treated population may die at twice the rate per uni




Odds Ratios Ors From The Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis Download Scientific Diagram




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
Or one could view the risk ratio and the odds ratio as approximations to the hazard ratio or rate ratio Rates and hazards can exceed 1, unlike risks, so there's no constraint on the hazard ratio, unlike the risk ratio Hazard ratios / rate ratios can therefore be constant over the entire range of baseline hazard / background rate Roger Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeableThis video wil help students and clinicians understand how to interpret hazard ratios




Relative Risk Wikipedia



1
$\begingroup$ @DWin the odds they speak of is a strange Ulike statistic that takes p/(1p) of the probability that a randomly selected case experiences an outcome faster than a randomly selected control But that p is related to the RR by RR = p/(1p) N0/N1 where N0 is the py exposure in the control, N1 for exposed if the outcome is rare, N0, N1 are very large and the ratio tends to 1Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notRelative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios?




Forest Plot An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
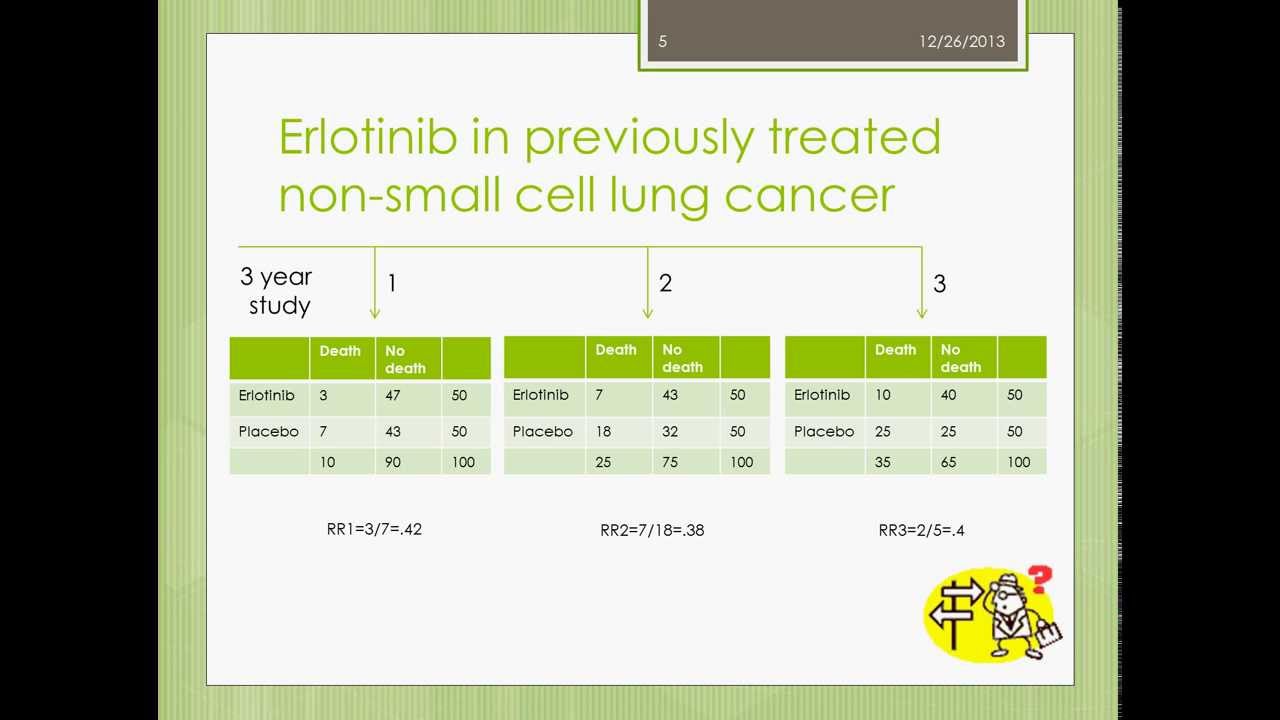



Hazard Ratios Fares Alahdab Md Youtube
Hazard ratio The hazard ratio in survival analysis is the effect of an exploratory?A logrank approach gives rise to a hazard ratio, and a variation of the Peto method for analysing timetoevent data gives rise to something in between The appropriate effect measure should beHazard ratio for progression or death, 034;



Hazard Ratio



Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Biostatistics Wiki Ucsf
Relative risks, odds ratio, hazard ratio relative risk/risk ratioratio of risk of an event occuring in the exposed group vs the unexposed grouprisk exposed risk unexposed in time to event or survival analysiscould be positive (cure) or negative (death)HR = hazard exposed/ hazard



Odds Ratio Vs




Pdf What Are Hazard Ratios




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube
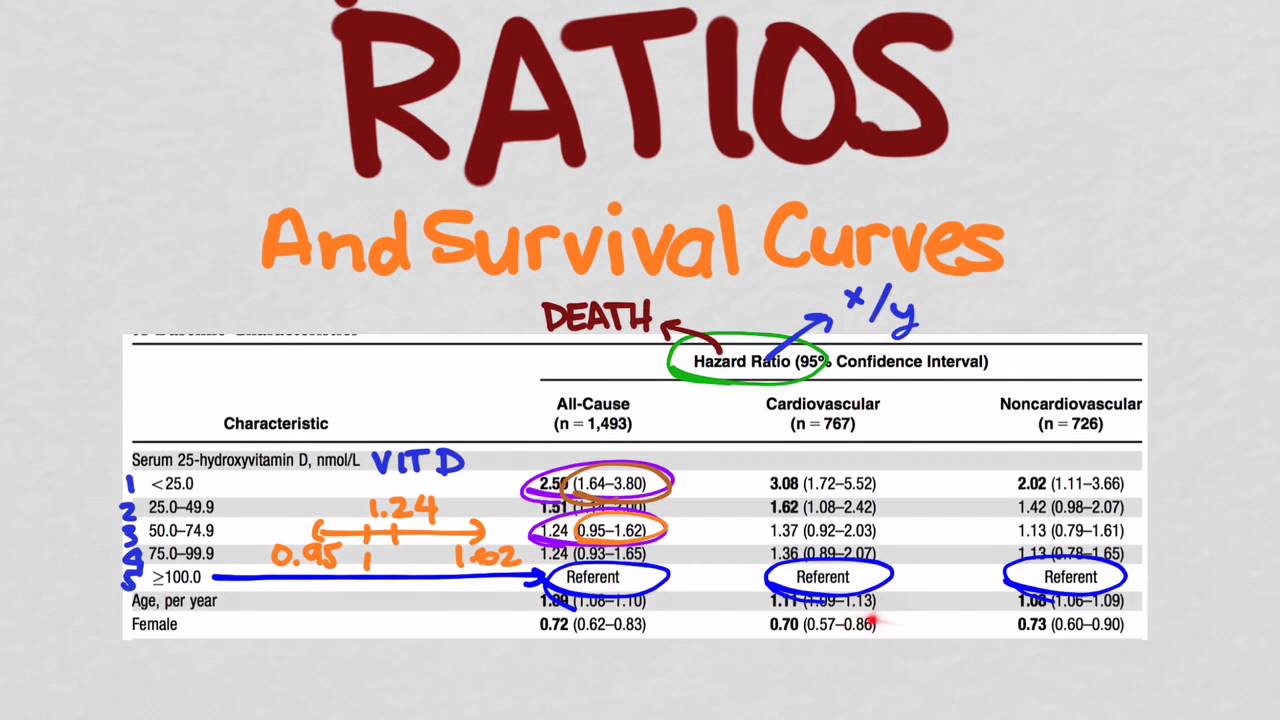



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science
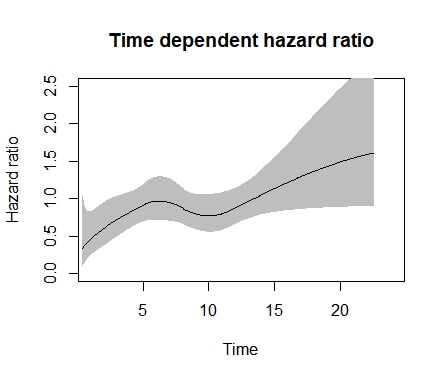



Hazard Ratio Plots With Non Linear Time Varying Effects In R Survival Analysis Datamethods Discussion Forum




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Odds Ratio And Hazard Ratio For Complications Download Table



Plos One Influence Of Clinicopathological Characteristics And Comprehensive Treatment Models On The Prognosis Of Small Cell Carcinoma Of The Cervix A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis




Flow Chart Of Inclusion Of Studies Hr Hazard Ratio Or Odds Ratio Download Scientific Diagram




Relative Risk Wikipedia



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




A Forest Plot Showing The Hazard Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
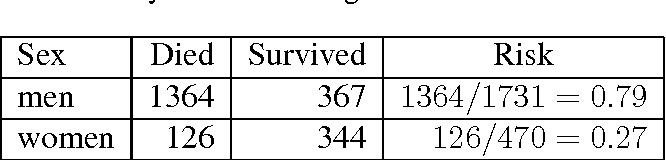



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect
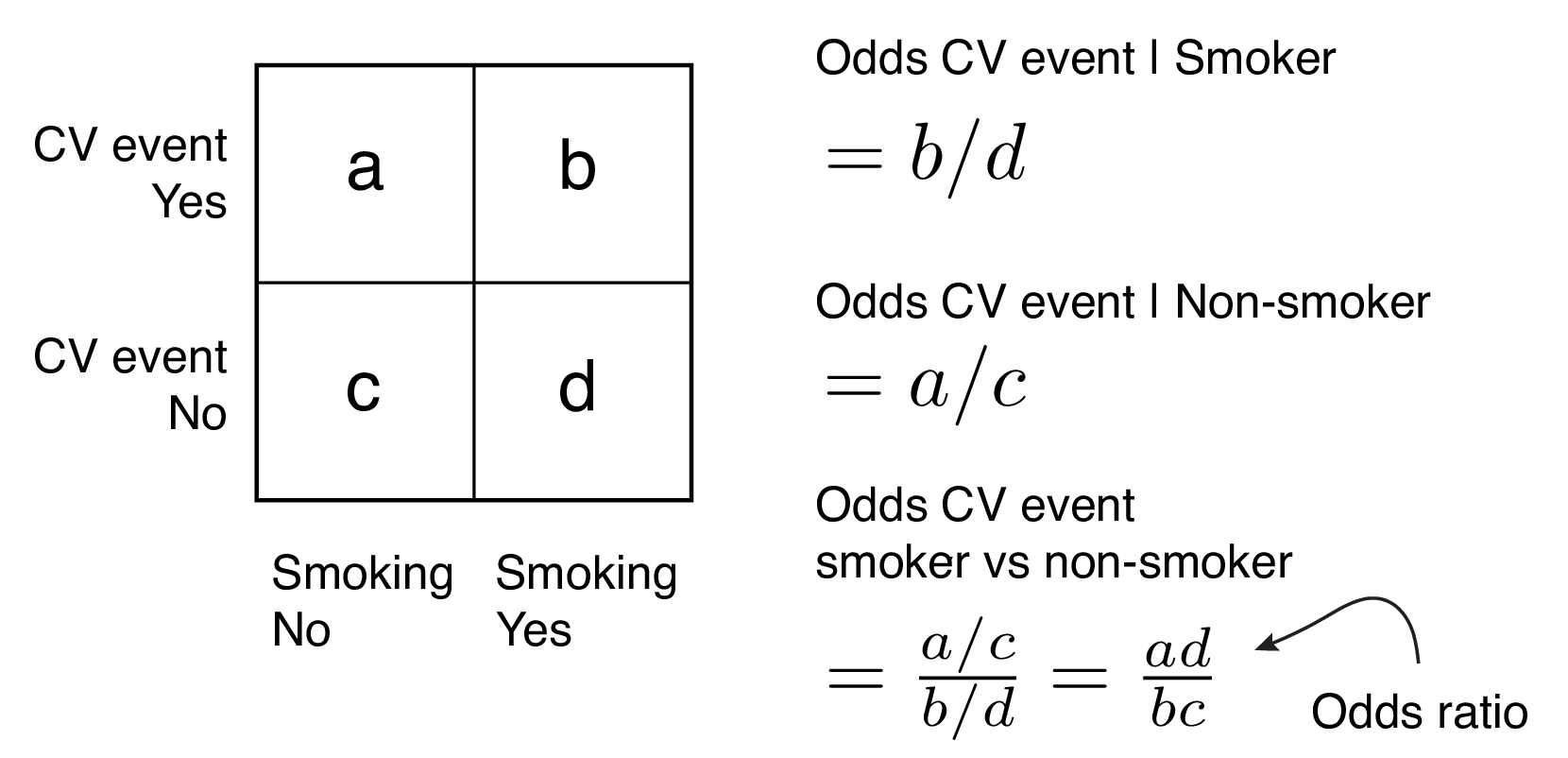



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Understanding The Endpoints In Oncology Overall Survival Progression Free Survival Hazard Ratio Censored Value




Calculating The Risk Ratio Odds Ratio And Risk Difference In A Randomised Controlled Trial Youtube




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Biostatistics Primer What A Clinician Ought To Know Hazard Ratios Sciencedirect
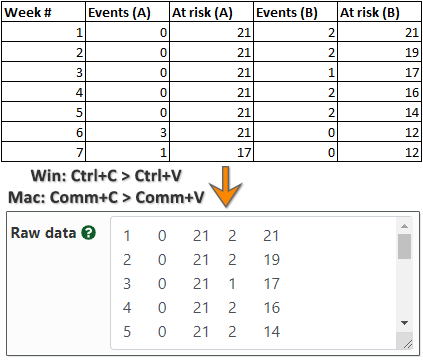



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value




Interpreting Hazard Ratios The Bmj
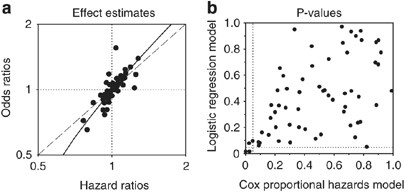



Cox Proportional Hazards Models Have More Statistical Power Than Logistic Regression Models In Cross Sectional Genetic Association Studies European Journal Of Human Genetics



Plos One Pcsk9 Loss Of Function Variants And Risk Of Infection And Sepsis In The Reasons For Geographic And Racial Differences In Stroke Regards Cohort




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Outcomes Shown For A Odds Ratio Analysis And B Hazard Ratio Download Scientific Diagram
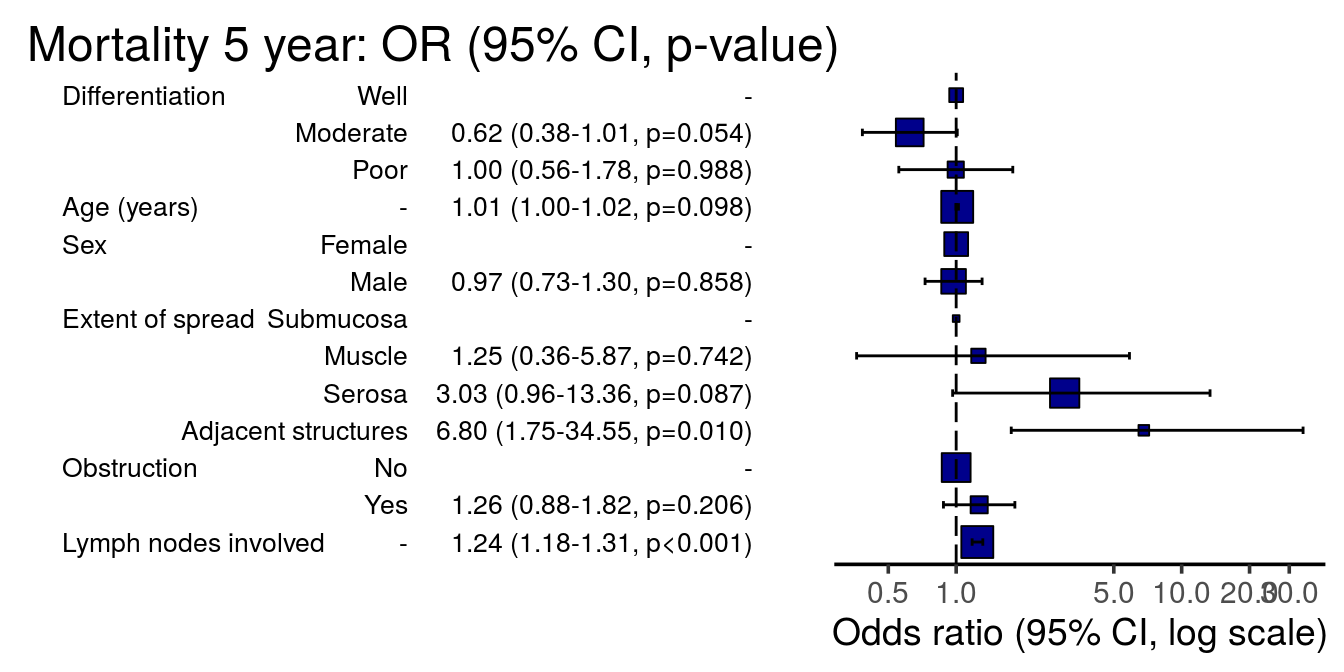



13 5 Odds Ratio Plot R For Health Data Science




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia




Confidence Intervals And P Values




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow
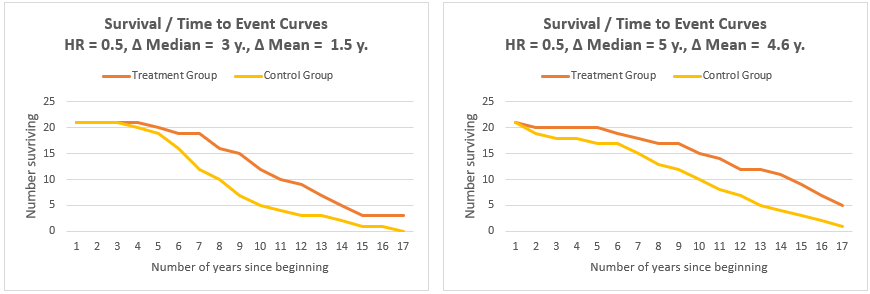



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value
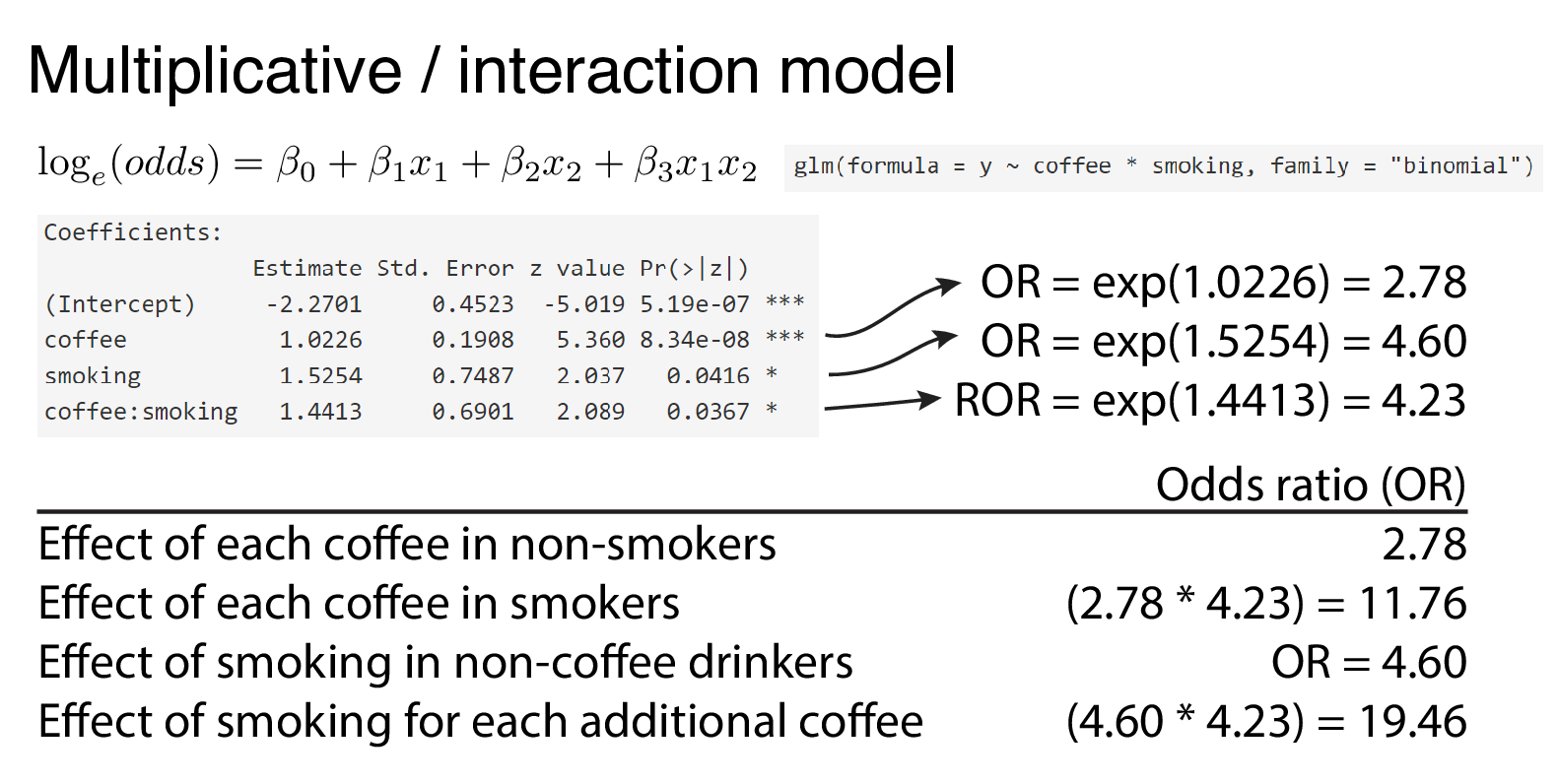



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect



Use And Interpret Chi Square In Spss




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow
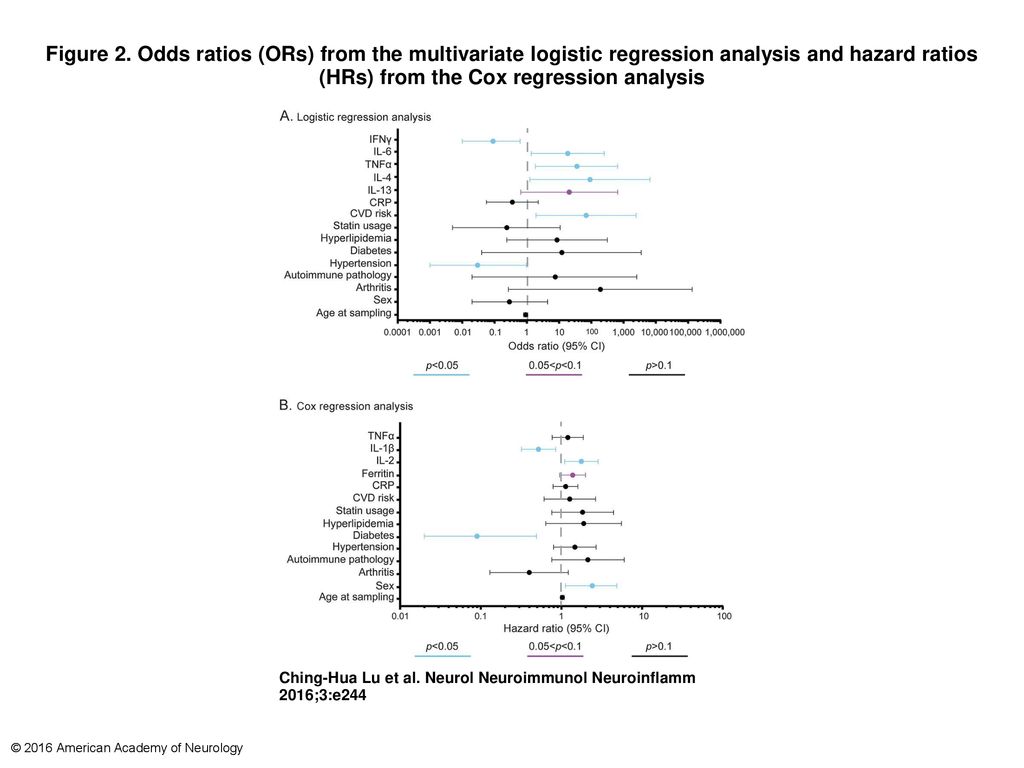



Figure 2 Odds Ratios Ors From The Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis And Hazard Ratios Hrs From The Cox Regression Analysis Odds Ratios Ors Ppt Download




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
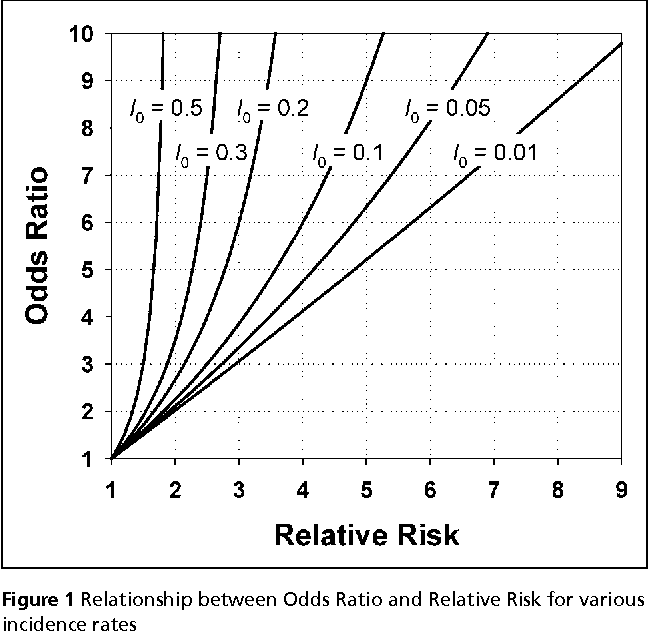



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Odds Ratio Article



Attributable Risk Formula




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
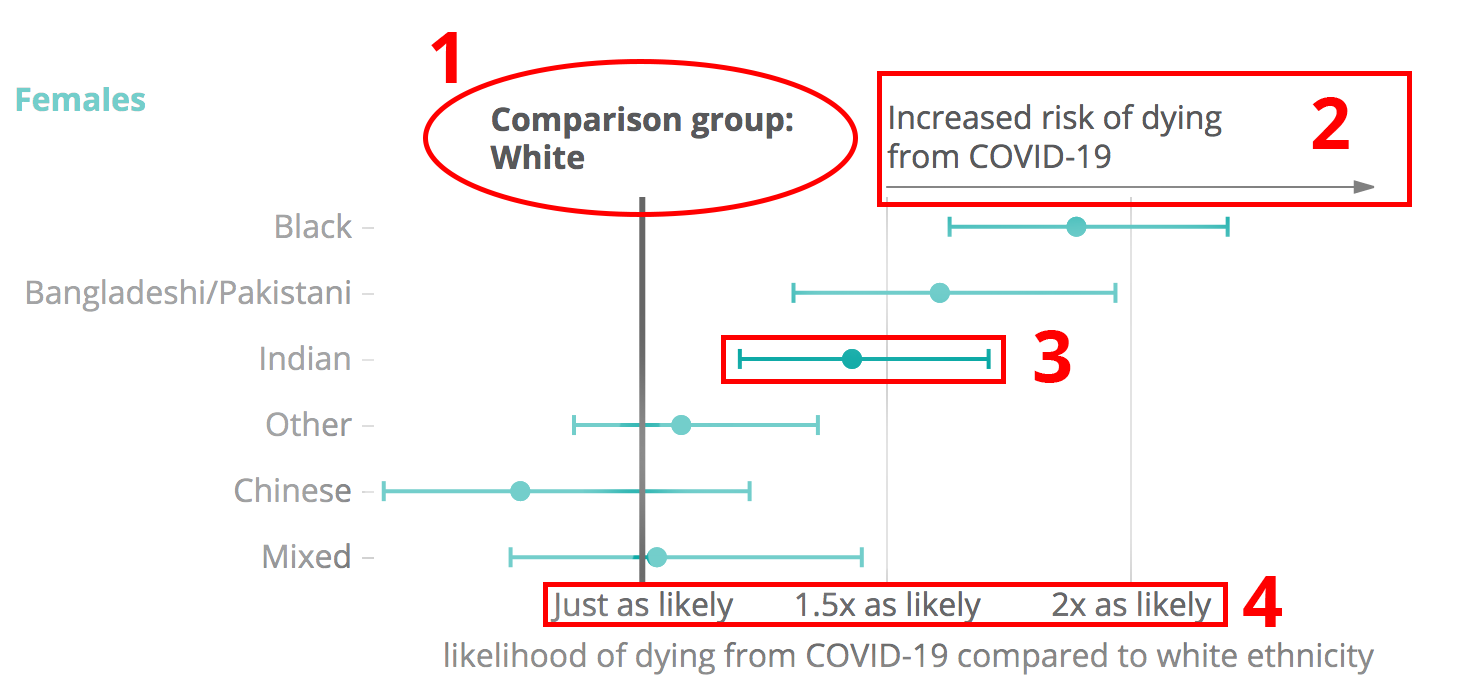



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



How To Remember The Differences Between Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Likelihood Ratio And In What Instances They Should Be Applied Quora



2




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Meta Analysis Odds Ratio




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



2




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research
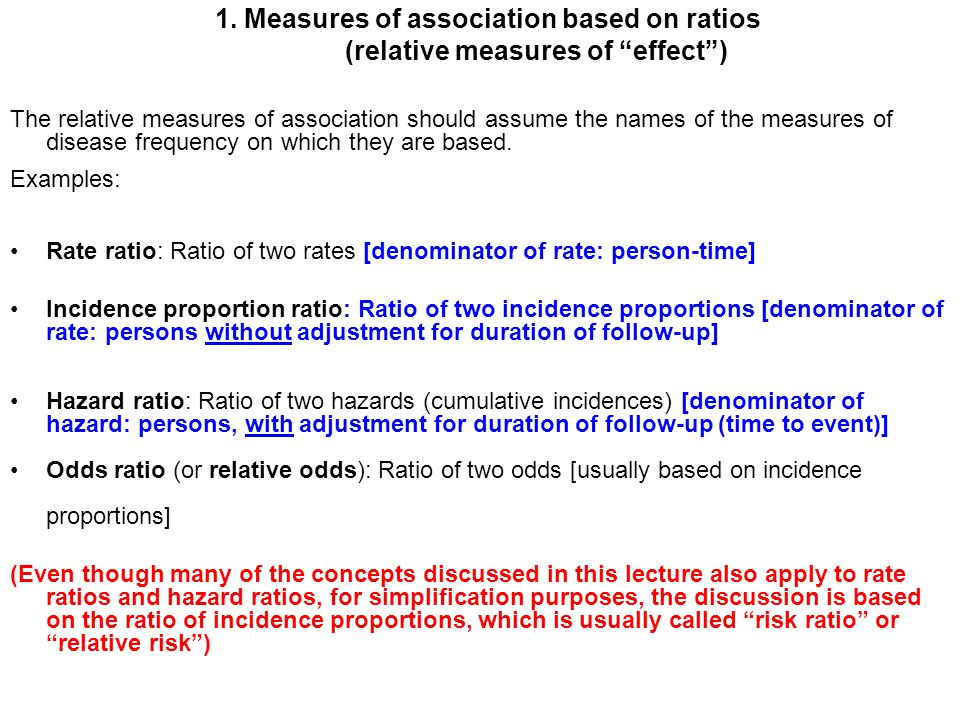



Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Hazard Ratios From Observational Studies Of Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting The Journal Of Thoracic And Cardiovascular Surgery



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿